Table of contents
sudo apt update # to update your ubuntu system
sudo apt install docker.io # to install docker setup on your ubuntu system
systemctl status docker # command to check status of docker engine
systemctl docker start # command to start docker services
docker images # command to print all the docker images present on the system
docker ps # command to print all the running conatainers on the system
docker ps -a # command to print all the running and stopped conatainers on the system
docker pull <images name> # to pull images from docker-hub
docker start <container name> # command to start a stopped container
docker stop <container name> # command to stop a running container
docker search <package name> # command to search a image on docker hub
docker attach <container name> # command to go inside a container
docker run <> <container name>
# <> options below
-d: detach/deamon
-e: environment
-i: interactive mode
-t: terminal
-p: port <port number>:<port number>
docker exec -it <container id> sh
-i: interactive
-t: terminal
sh: we do it get access
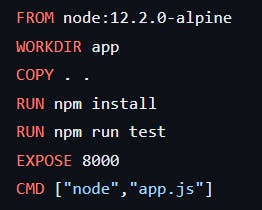
Dockerfile
Docker is a text file. It contains some set of instructions.
Automation of Docker image creation.
Docker Components
FROM: For the base image this command must be on top of the docker file.
RUN: To execute commands, it will create a layer of image.
MAINTAINER: Author/Owner/Description
COPY: Copy files from the local system (docker VM). We need to provide a source, and destination (we can't download files from the internet & any remote repo).
ADD: Similar to copy but it provides a feature to download files from the internet, also we extract files at the docker image side.
EXPOSE: To expose ports such as port 8080 for tomat, port 80 for nginx etc.
WORDIR: To set the working direction for a container.
CMD: To execute commands but during the container.
ENTRY POINT: Similar to CMD, but has a higher priority over CMD, first commands will be executed at ENTRYPOINT only.
ENV: Environment variables
ARG: Argument
Example: